Blended learning has emerged as a powerful educational approach that combines traditional classroom teaching with online learning methods. It offers a flexible and personalized learning experience for students, allowing them to learn at their own pace and providing teachers with tools to track and assess their progress. But mastering the art of blended learning requires more than just implementing technology in the classroom.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the nuances of blended learning and provide you with a roadmap to excel in this educational methodology. From understanding the key principles to designing effective online content, we will explore the essential elements that make blended learning successful. We will also discuss the different models and strategies that can be incorporated, such as station rotation, flipped classrooms, and personalized learning.
Whether you are an educator looking to enhance your teaching methods or a student looking for tips on how to navigate the world of blended learning, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and strategies to excel in this innovative learning environment. So, get ready to unlock the full potential of blended learning and revolutionize your educational experience.
What is blended learning?
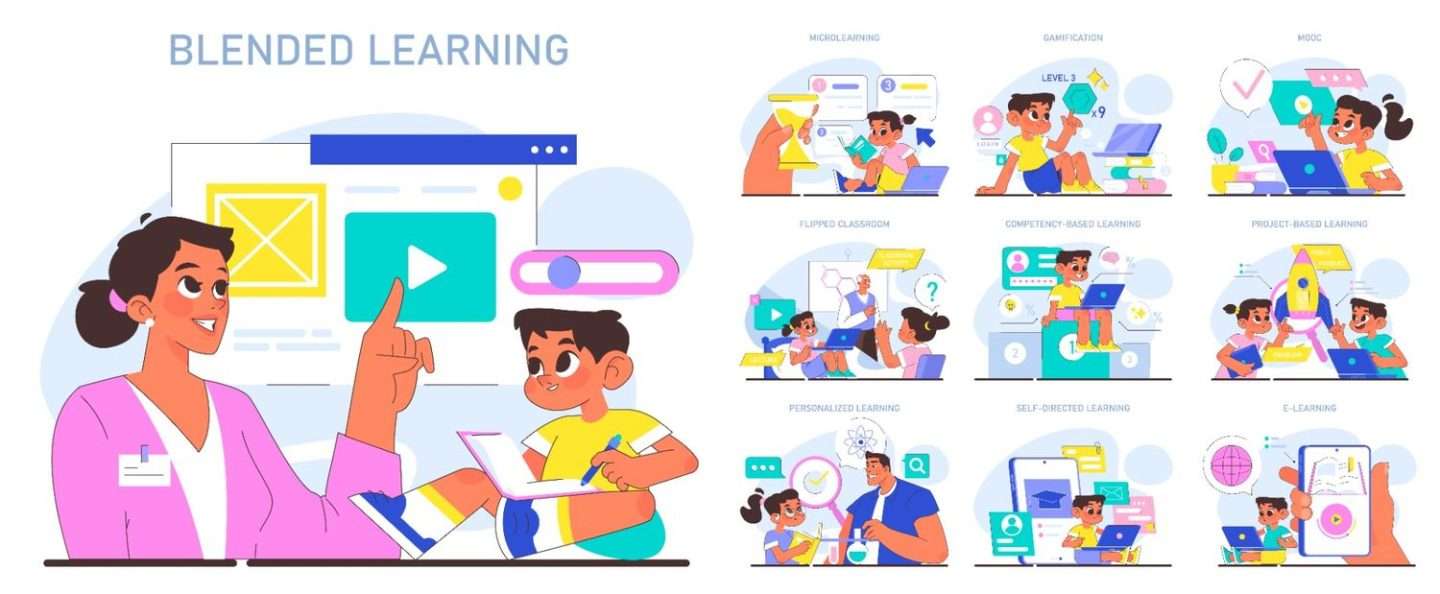
Blended learning is an educational approach that combines traditional face-to-face classroom instruction with online and digital learning components. This innovative methodology allows students to have a more personalized and flexible learning experience, where they can access course materials, engage in interactive activities, and receive feedback at their own pace. The blended learning model leverages the strengths of both in-person and digital learning, creating a dynamic and enriching educational environment.
The core idea behind blended learning is to create a seamless integration between the physical classroom and the digital realm. Instead of relying solely on one-way lectures or passive online content, blended learning encourages active participation, collaboration, and self-directed learning. Students can engage with course materials, communicate with their peers and instructors, and receive personalized support through a variety of digital tools and platforms.
By incorporating technology into the learning process, blended learning enables educators to tailor their instruction to the unique needs and learning styles of each student. This flexibility allows for more personalized feedback, targeted interventions, and opportunities for self-reflection and improvement. The blend of face-to-face and online elements also helps to foster a sense of community and engagement, as students can interact with their classmates and teachers both in person and through digital channels.
Advantages of blended learning
One of the primary advantages of blended learning is its ability to provide a more flexible and personalized learning experience. Students can access course materials, participate in online discussions, and complete assignments at their own pace, allowing them to better manage their time and tailor their learning to their individual needs. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for students with diverse learning styles, schedules, or geographic locations, as it enables them to engage with the content in a way that works best for them.
Blended learning also enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of instruction by leveraging the strengths of both in-person and online learning. In the physical classroom, students can engage in hands-on activities, collaborative discussions, and face-to-face interactions with their peers and teachers. Meanwhile, the online component provides access to a wealth of digital resources, multimedia content, and interactive learning tools that can deepen understanding and reinforce key concepts.
Furthermore, blended learning offers increased opportunities for data-driven decision-making and personalized feedback. By integrating learning management systems and analytics tools, educators can track student progress, identify areas of strength and weakness, and provide targeted interventions and support. This data-driven approach allows for more informed and responsive teaching, ultimately leading to improved student outcomes and a more engaging learning experience.
Hybrid learning models and approaches
Blended learning encompasses a range of models and approaches, each with its own unique characteristics and benefits. Understanding these different models can help educators and institutions select the most appropriate strategies for their specific learning environments and educational goals.
One of the most well-known blended learning models is the Flipped Classroom. In this approach, students engage with instructional content, such as video lectures or online readings, outside of the classroom. This allows class time to be dedicated to active learning activities, discussions, and collaborative projects, where students can apply and deepen their understanding of the material.
Another popular model is the Station Rotation, where students rotate through different learning stations within the classroom, with at least one station involving online or digital learning. This model encourages active engagement, personalized pacing, and small-group collaboration, while still maintaining a structured classroom environment.
The Individual Rotation model takes personalization a step further by allowing each student to have a customized schedule and learning path. Based on their individual needs and progress, students may rotate through different learning modalities, including online, face-to-face, and independent study, at their own pace.
Additionally, blended learning can be implemented through a Supplemental model, where online learning is used to supplement the traditional classroom instruction, or through an Enriched Virtual model, where students have required face-to-face learning sessions complemented by online learning activities.
Regardless of the specific model, the key to successful blended learning is to create a seamless integration between the in-person and digital components, ensuring that they work together to enhance the overall learning experience.
Designing a blended learning curriculum
Designing an effective blended learning curriculum requires a thoughtful and strategic approach that considers the unique needs and goals of the learning community. It’s essential to start with a clear understanding of the learning objectives, the target audience, and the available resources and constraints.
One of the critical steps in designing a blended learning curriculum is to carefully align the in-person and online components. This involves determining which topics and activities are best suited for face-to-face instruction and which can be effectively delivered through digital means. By striking the right balance, educators can create a cohesive and engaging learning experience that maximizes the strengths of both modalities.
When developing online content, it’s important to focus on creating interactive, multimedia-rich materials that encourage active engagement and self-directed learning. This may include video lectures, interactive simulations, discussion forums, and formative assessments that provide immediate feedback and opportunities for reflection. Incorporating adaptive learning technologies can also help personalize the online experience and tailor the content to individual student needs.
Equally important is the design of the in-person classroom activities. These sessions should be structured to build upon online learning, fostering deeper understanding, collaborative problem-solving, and hands-on application of the concepts. Strategies such as small-group discussions, project-based learning, and peer-to-peer feedback can help students actively engage with the material and develop essential skills.
Throughout the curriculum design process, it’s crucial to consider the assessment and evaluation methods that will be used to measure student learning and progress. Blended learning environments often require a combination of formative and summative assessments, including online quizzes, performance-based tasks, and in-person presentations or demonstrations. Leveraging data and analytics can also help educators identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to enhance the curriculum over time.
Technology tools for hybrid learning

The success of blended learning is heavily dependent on the effective integration of technology tools and platforms. These digital resources can enhance the learning experience, facilitate collaboration, and provide valuable data for instructors to optimize their teaching.
One of the foundational elements of blended learning is the learning management system (LMS). An LMS serves as the central hub for course materials, assignments, and communication, allowing students to access content, submit work, and engage with their peers and instructors. Popular LMS platforms, such as Canvas, Blackboard, and Moodle, offer a wide range of features, including discussion forums, video conferencing, and grading tools.
In addition to the LMS, blended learning can be enhanced through the use of various multimedia and interactive tools. Video conferencing platforms, such as Zoom or Microsoft Teams, enable real-time virtual interactions and collaborative activities. Asynchronous communication tools, like discussion boards or messaging apps, facilitate ongoing dialogue and knowledge sharing. Interactive whiteboards, such as Jamboard or Miro, can foster collaborative brainstorming and co-creation of content.
Adaptive learning technologies are another powerful tool in the blended learning arsenal. These platforms use algorithms and machine learning to personalize the learning experience, providing students with customized content, feedback, and support based on their individual needs and progress. Examples of adaptive learning tools include Knewton, McGraw-Hill Education’s ALEKS, and Pearson’s MyLab and Mastering.
To enhance the online components of blended learning, educators can leverage a variety of multimedia and content creation tools. Video creation platforms, like Screencast-O-Matic or Loom, allow instructors to record and share engaging video lessons. Interactive presentation tools, such as Prezi or Google Slides, can help create visually compelling and interactive content. Additionally, gamification and simulation platforms, like Kahoot! or Phet Interactive Simulations, can make the learning experience more engaging and immersive.
The effective integration of these technology tools, combined with a well-designed curriculum and pedagogical approach, can create a robust and dynamic blended learning environment that supports student success and empowers educators to deliver personalized and engaging instruction.
Best practices for implementing blended learning

Implementing a successful blended learning program requires a thoughtful and strategic approach that addresses both the technical and pedagogical aspects of the learning environment. Here are some best practices to consider when implementing blended learning:
- Establish a clear vision and goals: Begin by clearly defining the learning objectives, expected outcomes, and the role of blended learning in achieving those goals. Ensure that the hybrid learning approach aligns with the institution’s or department’s overall educational philosophy and strategic priorities.
- Provide comprehensive faculty and staff training: Invest in professional development opportunities that equip educators with the knowledge, skills, and confidence to design and facilitate effective blended learning experiences. This may include training on instructional design, technology integration, and effective online pedagogy.
- Ensure a robust technical infrastructure: Assess the institution’s technological capabilities, including internet connectivity, hardware, software, and technical support. Ensure that the necessary infrastructure is in place to support the seamless integration of digital tools and platforms.
- Prioritize student engagement and support: Design the hybrid experience with a strong focus on student engagement, motivation, and support. Incorporate opportunities for active learning, peer-to-peer collaboration, and regular feedback and communication with instructors.
- Implement a phased rollout: Consider a gradual, phased approach to implementing blended learning, starting with a pilot program or select courses. This allows for continuous improvement, feedback gathering, and refinement of the blended learning model before scaling it across the institution.
- Foster a culture of collaboration and innovation: Encourage a collaborative mindset among faculty, staff, and students. Encourage the sharing of best practices, the exploration of new technologies, and the continuous evaluation and improvement of the blended learning approach.
- Continuously evaluate and iterate: Regularly assess the effectiveness of the blended learning program, gathering feedback from students, instructors, and other stakeholders. Use data-driven insights to make informed decisions and continuously refine the curriculum, instructional strategies, and technology integration.
By following these best practices, institutions can create a robust and sustainable blended learning environment that enhances the educational experience, improves student outcomes, and empowers both learners and educators to thrive in the digital age.
Assessing student learning in a blended learning environment
Assessing student learning in a hybrid learning environment requires a thoughtful and comprehensive approach that goes beyond traditional assessment methods. Educators must consider the unique characteristics of blended learning and design assessment strategies that effectively measure student progress and achievement.
One of the key principles in assessing blended learning is to align the assessment methods with the learning objectives and the specific activities and content delivered through both the in-person and online components. This may involve a combination of formative and summative assessments, including quizzes, projects, presentations, and performance-based tasks.
Formative assessments play a crucial role in hybrid learning, as they provide ongoing feedback and opportunities for students to self-reflect and adjust their learning strategies. These assessments can take the form of online quizzes, discussion forum contributions, or interactive simulations, allowing instructors to monitor student progress and identify areas for improvement in real time.
Summative assessments, on the other hand, are used to evaluate the overall mastery of the course content and learning objectives. In a blended learning environment, these assessments may include a mix of online exams, capstone projects, or in-person presentations, depending on the specific learning goals and the balance between the digital and face-to-face components.
To ensure the effectiveness of assessments in a hybrid learning environment, it’s essential to leverage technology-enabled tools and platforms. Learning management systems (LMS) often provide a range of assessment features, such as online quizzes, rubric-based grading, and analytics dashboards, which can help streamline the assessment process and provide valuable data for instructors.
Additionally, the use of adaptive learning technologies and data-driven analytics can enhance the assessment process by providing personalized feedback, identifying knowledge gaps, and informing targeted interventions. By analyzing student performance data, educators can make data-driven decisions to improve the curriculum, adjust instructional strategies, and provide more personalized support to students.
Ultimately, the assessment of student learning in a blended learning environment should be a holistic and integrated process that aligns with the overall learning objectives, leverages the strengths of both in-person and online components, and provides meaningful feedback to support student success.
Challenges and solutions in blended learning
While blended learning offers numerous benefits, it also presents a unique set of challenges that must be addressed for a successful implementation. Understanding these challenges and proactively developing solutions can help ensure the long-term success of blended learning initiatives.
One of the primary challenges in blended learning is the potential for a digital divide, where students may have unequal access to the necessary technology, internet connectivity, or digital literacy skills. This can create a barrier to participation and lead to disparities in learning outcomes. To address this challenge, institutions should provide equitable access to technology, offer digital skills training, and explore solutions like loaner programs or internet subsidies for students in need.
Another challenge is the need for effective faculty and staff development to ensure that educators are equipped with the knowledge and skills to design and facilitate blended learning experiences. Investing in comprehensive professional development, including training on instructional design, online pedagogy, and technology integration, can help build the necessary competencies and confidence among faculty.
Maintaining student engagement and motivation in a blended learning environment can also be a challenge, as the balance between in-person and online components can be delicate. Strategies such as incorporating interactive activities, fostering a sense of community, and providing regular feedback and support can help keep students engaged and invested in the learning process.
Ensuring the quality and consistency of the blended learning experience across different courses or sections can also be a significant challenge. Implementing clear guidelines, standardized course templates, and centralized support resources can help maintain the quality and coherence of the hybrid learning program.
Finally, the effective integration of technology tools and platforms can present logistical and technical challenges, such as compatibility issues, data privacy concerns, and the need for ongoing technical support. Addressing these challenges requires a well-planned technology infrastructure, robust IT support, and a proactive approach to addressing emerging technological needs.
By acknowledging these challenges and proactively developing solutions, institutions can create a blended learning environment that is accessible, engaging, and effectively supported, ultimately leading to improved student outcomes and a more enriching educational experience.
Professional development for educators in blended learning
Effective implementation of blended learning requires a significant investment in professional development for educators. As the role of teachers evolves in a blended learning environment, it is crucial to provide them with the necessary knowledge, skills, and support to excel in this innovative educational approach.
One of the key aspects of professional development for hybrid learning is training on instructional design. Educators need to understand how to effectively integrate online and face-to-face components, create engaging and interactive digital content, and align the learning activities with the desired learning outcomes. This may involve workshops, webinars, or one-on-one coaching sessions that cover topics such as multimedia creation, learning management system usage, and the principles of effective online pedagogy.
In addition to instructional design, educators must also develop competencies in technology integration. This includes not only the technical skills to use various digital tools and platforms but also the ability to seamlessly incorporate them into their teaching practice. Professional development opportunities should cover the effective use of learning management systems, video conferencing software, interactive whiteboards, and other educational technologies that support blended learning.
Fostering a growth mindset and a culture of innovation is another crucial aspect of professional development for blended learning. Educators should be encouraged to experiment with new approaches, share best practices, and continuously reflect on their teaching methods. This can be facilitated through peer-to-peer learning communities, collaborative lesson planning, and opportunities for feedback and reflection.
Furthermore, professional development should address the unique challenges and considerations of student engagement and assessment in a blended learning environment. Educators need to learn strategies for maintaining student motivation, providing personalized feedback, and designing effective assessments that align with the blended learning model.
To ensure the sustainability and ongoing improvement of the blended learning program, it is essential to provide continuous professional development opportunities. This may include regular check-ins, refresher courses, and opportunities for educators to share their experiences and learn from one another. By investing in the professional growth of educators, institutions can create a thriving blended learning ecosystem that supports both student and teacher success.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of blended learning is a transformative journey that can revolutionize the educational landscape. By seamlessly integrating traditional classroom instruction with the power of digital technologies, blended learning creates a dynamic and personalized learning experience that empowers both students and educators.
In this comprehensive guide, we have explored the key principles, models, and strategies that underpin successful blended learning initiatives. From designing effective curricula and leveraging cutting-edge technology tools to implementing best practices and addressing unique challenges, we have provided a roadmap for educators and institutions to excel in this innovative educational approach.
As the education landscape continues to evolve, the mastery of blended learning will become increasingly essential. By embracing this transformative methodology, educators can unlock new possibilities for student engagement, personalized learning, and data-driven decision-making. Moreover, students will have the opportunity to develop the critical skills and adaptability needed to thrive in the digital age.
Whether you are an experienced educator or a student embarking on a blended learning journey, this guide has equipped you with the knowledge and strategies to navigate the complexities of this dynamic educational landscape. By implementing the principles and best practices outlined here, you
📣Want to check out more blogs like this? Visit our blogs!